2D-feature embedding
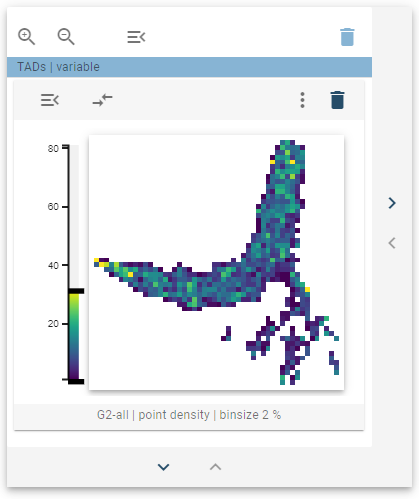
The 2D-feature embedding widget can be used to display the distribution of genomic regions regarding a 2D-genomic feature. It represents a 2-dimensional embedding of the genomic regions as a heatmap of points.
Suitable data
The 2D-feature embedding widget is suitable for any genomic dataset that can be represented using a multiresolution cooler file. This is mostly suitable for Hi-C data but can include other data sets that assign a value to a tuple of genomic coordinates.
Preprocessing algorithm
In general, the preprocessing for data to be displayed in the 2D-feature embedding widget happens together with preprocessing for the 2D-average widget, and thus many of the steps are shared.
Point-regions
During the preprocessing state, snippets of the underlying interaction matrix are extracted from the mcool file for each entry in the genomic region set, with different window sizes. Then, these images are downsampled and flattened into a “feature representation”. The resulting feature matrix has the following shape:
| Image feature 1 | … | Image feature k | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomic region 1 | 0.1 | … | 1.5 |
| … | … | … | … |
| Genomic region n | 0.8 | … | 0.4 |
Where k refers to the number of pixels in the downsampled images and n refers to the number of genomic regions in the respective region set. Following this step, umap is used with default parameters to get a 2-dimensional embedding of the genomic regions.
Additionally, the regions are clustered using k-means clustering into two different cluster-sets (one with a high number of clusters and one with a low number of clusters; see the configuration section on how to change these numbers). A cluster “thumbnail” that represents the average image within this cluster is saved and then used to display information thumbnails (see the visualization section for more details).
Interval-regions
Interval features are treated exactly as point features, except that images are scaled to a common size before processing.
Visualization
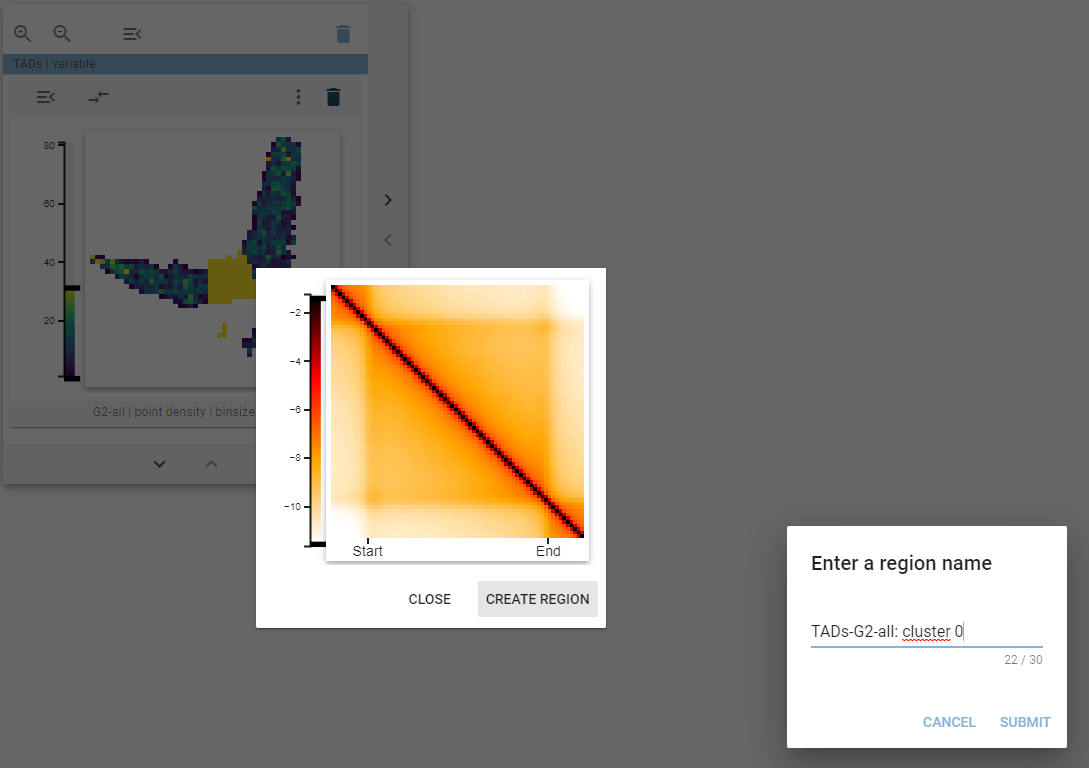
The distribution of the genomic regions regarding a 2D feature is visualized as a 2D-histogram, with the density of points being displayed using a colormap. This widget defines a tooltip that will display a cluster thumbnail that represents the average image within that cluster when hovered over the points.
Widget controls
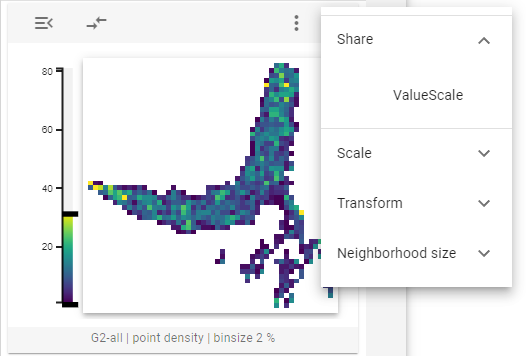
The 2D-feature embedding widget defines four controls on the widget and one control on the thumbnail tooltip.
Sharing
The sharing controls allow you to select whether all thumbnail representations should share a common color scale or not.
Scale
The scale widget control allows to switch between ICCF values (I teratively C orrected C ontact F requency) and Observer/expected values, which were normalized to the genome-wide distance-dependent decay of contact frequency.
Transform
The transform widget control allows you to select whether the values displayed in the thumbnails should be log-transformed or not.
Neighborhood size
One can use the neighborhood size option to choose whether to display large or small clusters (for defining the respective sizes, see the configuration section) in the thumbnail tooltip.
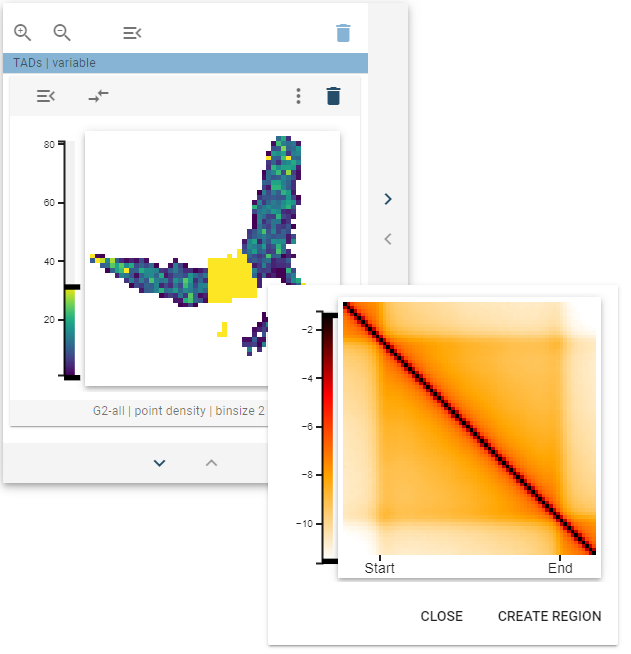
Create new region
If one of the highlighted clusters is interesting and you want to explore them further, you can create a new genomic region set representing the highlighted regions. For this, when the thumbnail tooltip is shown, click, and the “Create new region” button will appear. After clicking that button, a dialog pops up that lets you define the name for your new region set.